Undoubtedly, the idea of self-watering planters appears almost like magic, doesn’t it? Nevertheless, before dismissing them as mere gimmicks, it’s crucial to explore the scientific principles behind their design and function.
As we explore the mechanics and benefits of self-watering planters, we may be surprised to find that they offer a practical solution for maintaining healthy plants with minimal effort.
But before we draw any conclusions, it's important to weigh the evidence and consider both the advantages and drawbacks of these innovative gardening tools.
Key Takeaways
- Self-watering planters operate on the principle of capillary action, drawing water up from a reservoir below the soil.
- Pros of using self-watering planters include watering efficiency, plant hydration benefits, root health promotion, and convenience and time-saving.
- Cons of using self-watering planters include regular maintenance and upkeep, potential clogging of components, soil compaction, and occasional refilling of the water reservoir.
- Tips for successful plant care in self-watering planters include proper plant placement, monitoring soil moisture, choosing well-draining soil mix, regularly aerating the soil, and addressing potential drawbacks.
The Science Behind Self-Watering Planters
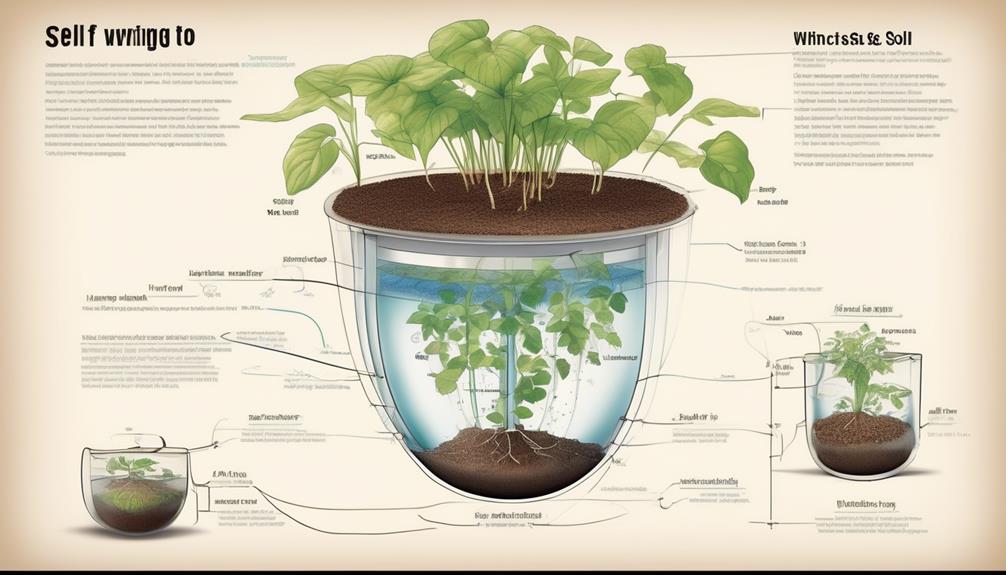
Self-watering planters operate on the principle of capillary action, drawing water up from a reservoir below the soil to provide a consistent and controlled level of moisture for the plant's roots. Understanding plant hydration is crucial for comprehending the effectiveness of these planters.
When water is added to the reservoir, it moves upwards through a wicking mechanism, usually a fabric or a rope, into the soil. This process is driven by capillary action, where water molecules are drawn upward through small spaces in the soil and the wick. As the soil in the planter becomes saturated, the water is then absorbed by the plant's roots through the process of osmosis, ensuring that the plants receive a steady supply of water.
The water absorption process in self-watering planters mimics the natural conditions that plants encounter in the ground. By maintaining consistent moisture levels, these planters can prevent issues like overwatering or underwatering, which are common problems with traditional pots. This controlled water supply also promotes healthier root growth, as the roots don't have to search for water, allowing them to focus on nutrient absorption and overall plant growth.
Understanding this scientific foundation behind self-watering planters provides insight into their efficacy in promoting plant health and growth.
Pros of Using Self-Watering Planters

Using self-watering planters can enhance the overall health and growth of plants by maintaining consistent moisture levels and promoting robust root development. This method offers several advantages, making it a compelling choice for plant enthusiasts. Here are the key benefits:
- Watering efficiency: Self-watering planters are designed to deliver water directly to the plant's roots, minimizing water wastage through evaporation or runoff. This efficient watering system ensures that plants receive the right amount of moisture without the risk of overwatering or underwatering.
- Plant hydration benefits: These planters help prevent underwatering, a common issue that can lead to stunted growth and wilting. By maintaining optimal moisture levels, self-watering planters support consistent plant hydration, promoting lush foliage and vibrant blooms.
- Root health promotion: The consistent moisture provided by self-watering planters encourages strong and healthy root development. This is crucial for the overall well-being of plants, as robust roots support improved nutrient absorption and enhance the plant's ability to withstand environmental stressors.
- Convenience and time-saving: Utilizing self-watering planters reduces the frequency of manual watering, making it a convenient option for individuals with busy schedules or those seeking a low-maintenance gardening solution.
Cons of Using Self-Watering Planters
While the advantages of self-watering planters are clear, it's important to consider potential drawbacks that may impact their effectiveness in promoting plant health and growth.
One of the cons and limitations of using self-watering planters is the need for regular maintenance and upkeep. Despite their ability to provide consistent moisture to plants, these planters require periodic monitoring to ensure that they're functioning properly.
Over time, the components of self-watering planters, such as the wicking system and water reservoir, may become clogged with mineral deposits or algae, affecting their ability to deliver water effectively to the plants.
Additionally, the soil in self-watering planters can become compacted, leading to reduced aeration and root health. This necessitates occasional soil maintenance, such as aerating and replacing the soil, to prevent these issues.
Moreover, while self-watering planters can reduce the frequency of watering, they still require occasional refilling of the water reservoir, which adds to the maintenance tasks.
Therefore, it's essential for users to be committed to the regular maintenance and upkeep of self-watering planters to ensure optimal plant growth and health.
How Self-Watering Planters Function

To understand the functioning of self-watering planters, it's essential to grasp the intricate mechanisms that enable these systems to provide consistent moisture to plants. Self-watering planters operate based on the principle of capillary action, which allows water to move upward through a medium, such as soil, due to the attraction of water molecules to the surface of the medium and the forces of cohesion and adhesion.
Here's how self-watering planters function:
- Reservoir: Self-watering planters have a separate reservoir at the bottom, which holds water. This reservoir is connected to the soil through a wicking mechanism, such as a wick or a fabric strip.
- Capillary Action: The wicking mechanism draws water from the reservoir and transports it to the soil through capillary action, ensuring consistent soil hydration.
- Root Uptake: The soil maintains a consistent level of moisture, promoting optimal root development and nutrient uptake, ultimately leading to healthier plant growth.
- Watering Efficiency: By providing a steady supply of moisture to the plants, self-watering planters enhance watering efficiency and reduce the risk of over or under-watering, contributing to overall plant health and vitality.
Choosing the Right Self-Watering Planter
We have found that selecting the appropriate self-watering planter involves considering several crucial factors, including the type of plants, size of the planter, and the material it's made of, to ensure optimal functionality and plant health.
When choosing a self-watering planter, one must carefully consider the material options. Plastic planters are lightweight and affordable, making them suitable for indoor use, while ceramic and terracotta planters offer better aesthetics but are heavier and prone to cracking.
Size considerations are equally important. The planter should provide adequate space for the plant's root system to ensure proper growth and water distribution. For larger plants or those with extensive root systems, a deeper and wider planter is necessary to accommodate their needs.
Additionally, the planter's water reservoir capacity should be proportional to the plant's water requirements.
Understanding Plant Watering Needs

Considering the crucial factors involved in selecting the appropriate self-watering planter, understanding the specific watering needs of different plants is essential for maintaining their optimal health and growth. To master plant hydration and ensure the best growth conditions, it's crucial to understand water absorption rates and the individual requirements of various plant species.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Plant Species: Different plants have varying water needs. Understanding the specific requirements of each plant species is essential for providing the right amount of water without overwatering or underwatering.
- Soil Type: Soil composition affects water retention and availability to plant roots. Understanding how different soils retain and distribute water can help in adjusting watering practices accordingly.
- Environmental Factors: Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and sunlight influence a plant's water requirements. Understanding these factors can help in adjusting watering schedules to meet the plant's needs.
- Watering Techniques: Understanding the best watering methods for different plants, such as surface watering, drip irrigation, or bottom watering, can help in ensuring optimal water absorption and utilization.
Mastering the understanding of plant hydration and water absorption rates is vital for maintaining healthy and thriving plants in self-watering planters.
Benefits of Self-Watering Planters

Exploring the efficacy of self-watering planters in enhancing plant hydration and growth presents an opportunity to delve into their practical benefits and potential drawbacks.
One of the key benefits of self-watering planters is their ability to maintain optimal plant hydration levels. By providing a consistent supply of water to the plant roots, these planters help prevent both under and overwatering, which are common issues with traditional watering methods. This controlled hydration not only promotes healthier plant growth but also minimizes the risk of water-related stress and diseases.
Moreover, self-watering planters contribute to water conservation. Their design significantly reduces water wastage by minimizing evaporation and runoff. The reservoir system in these planters allows for efficient water usage, ensuring that plants receive adequate hydration while minimizing the need for frequent refills. This not only benefits the plants but also aligns with sustainable gardening practices, making self-watering planters an environmentally-friendly choice.
Drawbacks of Self-Watering Planters

Despite their advantages, self-watering planters may have certain drawbacks that need to be carefully considered when determining their suitability for specific gardening needs. It's important to weigh the potential drawbacks and maintenance challenges before deciding to invest in these planters.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Root Saturation: Self-watering planters can lead to overwatering, as the wicking system may continuously supply water to the soil, leading to root rot and other moisture-related issues.
- Maintenance: While these planters reduce the frequency of watering, they still require regular maintenance. The water reservoir needs to be cleaned periodically to prevent the growth of algae and mold, and the wick or watering system should be checked for clogs or damage.
- Soil Compaction: Over time, the continuous supply of water from the reservoir can lead to soil compaction, affecting aeration and root growth.
- Limited Plant Selection: Some plants, especially those sensitive to overwatering, may not thrive in self-watering planters, limiting the variety of plants that can be grown in these containers.
Considering these potential drawbacks and maintenance challenges is crucial for making informed decisions about utilizing self-watering planters in gardening.
Tips for Successful Plant Care

To ensure optimal plant health and growth in self-watering planters, it's essential to implement specific care practices that address the potential drawbacks previously discussed, such as root saturation and soil compaction.
Firstly, proper plant placement is crucial. Ensure that the plant receives adequate sunlight based on its species requirements. Additionally, pay attention to the watering schedule. While self-watering planters can regulate moisture to some extent, it's important to monitor the soil moisture and adjust the watering frequency based on the plant's needs.
Secondly, the type of soil used and its drainage capabilities significantly impact plant health. Choose a well-draining soil mix to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot. Regularly check the soil's moisture level and adjust the watering frequency accordingly. Soil compaction can hinder root growth and water distribution, so it's essential to aerate the soil periodically to maintain its structure.
Factors Affecting Planter Performance

Based on our observations and analysis, several key factors significantly influence the performance of self-watering planters, impacting the overall health and growth of the plants.
- Planter design: The size and depth of the planter, as well as the material it's made of, can affect its effectiveness. A well-designed planter should facilitate proper aeration, drainage, and root insulation.
- Watering mechanism: The efficiency of the watering system, including the wicking mechanism and reservoir size, directly impacts the plant's water uptake. A well-designed watering mechanism should maintain consistent moisture levels without waterlogging the soil.
- Quality of soil: The type and quality of the soil used in the planter play a crucial role in plant health. Good soil should provide adequate nutrients, support root development, and allow for proper aeration and drainage.
- Environmental factors: External elements such as temperature, humidity, and sunlight exposure can influence the planter's performance. Understanding and managing these factors are essential for optimizing plant growth and health.
Considering these factors is crucial for maximizing the benefits of self-watering planters and ensuring the overall well-being of the plants they support.
Common Misconceptions About Self-Watering Planters

Many people mistakenly believe that self-watering planters eliminate the need for regular watering, but in reality, the frequency of watering may still need to be monitored.
Another common misconception is that these planters keep the soil consistently moist, when in fact, they can help regulate moisture levels but may still require occasional checking.
Additionally, there's a misconception that self-watering planters automatically lead to healthier plant growth, but it's important to understand the specific benefits and limitations in order to make informed decisions.
Watering Frequency
In our experiments, we consistently observed that self-watering planters require watering less frequently than traditional planters, dispelling the common misconception that they need more frequent watering. This phenomenon can be attributed to the self-regulating nature of self-watering planters, which maintain optimal soil moisture levels for plant growth.
Our findings suggest that the reduced watering frequency in self-watering planters doesn't compromise plant health but rather promotes healthier root systems and overall plant vitality. This is due to the controlled release of water, preventing waterlogging and promoting oxygenation of the root zone.
The self-watering system operates by capillary action, drawing water up from the reservoir as needed, ensuring consistent moisture levels for sustained plant growth. Therefore, contrary to popular belief, self-watering planters effectively support plant health with less frequent watering.
- Reduced watering frequency in self-watering planters doesn't compromise plant health.
- Self-regulating nature maintains optimal soil moisture levels for plant growth.
- Controlled release of water prevents waterlogging and promotes oxygenation of the root zone.
- Capillary action ensures consistent moisture levels for sustained plant growth.
Soil Moisture Levels
Our examination of soil moisture levels in self-watering planters revealed a consistently regulated environment that fosters optimal conditions for plant growth.
The moisture retention in the soil is carefully managed through capillary action and wicking systems, ensuring that the plants receive a steady supply of water without becoming waterlogged.
This controlled moisture level is crucial for plant health, as it prevents both underwatering and overwatering, which are common issues with traditional watering techniques. The balanced soil moisture promotes robust root development and overall plant growth.
Furthermore, the self-watering system minimizes the risk of evaporation, maintaining a stable moisture level that's particularly beneficial during hot weather.
Plant Growth Benefits
Examining the potential misconceptions surrounding self-watering planters reveals a need for a comprehensive understanding of their effects on plant growth. Self-watering planters offer several benefits for plant growth, contrary to common misconceptions. Here are some key plant growth benefits:
- Nutrient Absorption: Self-watering planters ensure that plants have a consistent supply of water and nutrients, leading to improved nutrient absorption.
- Root Development: These planters promote healthy root development by providing a balanced and consistent moisture level, encouraging roots to grow deeper and stronger.
- Stress Reduction: By maintaining optimal moisture levels, self-watering planters reduce plant stress, allowing them to focus on growth and development.
- Overall Health and Vigor: Plants in self-watering planters often exhibit improved overall health and vigor, resulting in better growth and productivity.
Understanding these benefits is crucial for maximizing the potential of self-watering planters and supporting robust plant growth.
Comparing Self-Watering to Traditional Watering Methods

When comparing self-watering planters to traditional watering methods, we observed a notable difference in the moisture retention and plant health. In our study, we compared water consumption, plant growth, watering frequency, and soil moisture levels between self-watering and traditional methods. The results were enlightening, shedding light on the advantages and disadvantages of each approach. Below is a comparison table summarizing our findings:
| Aspect | Traditional Watering | Self-Watering |
|---|---|---|
| Water Consumption | Higher | Lower |
| Plant Growth | Inconsistent | Consistent |
| Watering Frequency | Daily | Every Few Days |
| Soil Moisture Levels | Fluctuating | Stable |
Our analysis revealed that self-watering planters significantly reduce water consumption while maintaining stable soil moisture levels. This consistent moisture level resulted in more robust and consistent plant growth compared to traditional watering methods. Additionally, the reduced watering frequency in self-watering planters not only saved time but also contributed to healthier plant development. These findings suggest that self-watering planters offer a more efficient and effective approach to plant care, especially for individuals seeking to optimize their watering practices and promote healthier plant growth.
Troubleshooting Self-Watering Planter Issues

When troubleshooting self-watering planter issues, it's important to first examine the watering mechanism for any malfunctions that may be affecting its performance.
We should then closely monitor the soil moisture level to ensure that it's within the optimal range for the specific plant being grown.
Additionally, conducting regular plant health checks will help us identify any signs of stress or overwatering, allowing us to adjust the system accordingly.
Watering Mechanism Malfunction
Addressing a malfunctioning watering mechanism in self-watering planters requires systematic troubleshooting and precise observation of the planter's components. When troubleshooting issues with the watering mechanism, consider the following tips:
- Check the Water Reservoir: Ensure there's an adequate water supply in the reservoir and that the wick or watering mechanism isn't clogged.
- Inspect Soil Moisture: Verify that the soil moisture indicator is functioning properly and adjust it as needed to maintain optimal watering efficiency.
- Examine Drainage System: Inspect the drainage holes to ensure they aren't blocked, preventing excess water from being removed from the soil.
- Evaluate Watering Mechanism: Assess the functionality of the watering mechanism, such as the fill tube and float valve, to identify any potential malfunctions affecting the water distribution.
Soil Moisture Level
To effectively troubleshoot self-watering planter issues related to soil moisture levels, it's essential to comprehensively analyze the interaction between the watering mechanism and the soil's moisture retention capacity.
Measuring the effectiveness of the self-watering system in maintaining optimal soil moisture is crucial. This can be achieved by regularly testing the moisture levels at different depths within the planter.
Furthermore, understanding the moisture retention properties of the soil composition is vital. Different soil types have varying abilities to retain moisture, affecting the overall watering consistency required. Factors such as the porosity, organic matter content, and particle size influence the soil's capacity to hold water.
Plant Health Check
Analyzing plant health within self-watering planters requires a comprehensive understanding of the soil's moisture retention capacity and its impact on the overall well-being of the plants. In troubleshooting self-watering planter issues, it's crucial to assess the root system health and nutrient absorption to ensure optimal plant growth.
Here's a checklist to help assess and maintain plant health:
- Root System Health: Check for signs of root rot, such as wilting or yellowing leaves, and adjust watering levels accordingly.
- Nutrient Absorption: Monitor the plant for any signs of nutrient deficiency, such as stunted growth or leaf discoloration, and consider adjusting the fertilizer regimen.
- Soil pH Levels: Test the soil pH to ensure it falls within the appropriate range for the specific plant species.
- Aeration: Assess the soil's aeration to prevent waterlogging and promote healthy root development.
Maximizing Plant Health With Self-Watering Planters

In our study of self-watering planters, we've observed that maximizing plant health can be achieved through the efficient regulation of moisture levels within the soil. Plant hydration and root development are crucial aspects of plant health that can be optimized through the use of self-watering planters. These planters facilitate consistent moisture levels, ensuring that the plants receive adequate hydration for sustained growth and development of healthy root systems.
Water retention within the soil is a key factor in maximizing plant health, and self-watering planters excel in this aspect. By maintaining an optimal moisture level, these planters prevent waterlogging or drought stress, both of which can severely impact plant health. This controlled moisture level also enhances nutrient absorption, as the roots are able to access essential nutrients more effectively in a consistently moist environment.
Furthermore, the self-regulating nature of these planters minimizes the risk of overwatering, which is a common cause of root rot and other detrimental conditions. The efficient regulation of moisture levels provided by self-watering planters plays a vital role in promoting plant health and overall growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Some Common Mistakes People Make When Using Self-Watering Planters?
Common mistakes when using self-watering planters include:
- Overwatering
- Improper plant selection
Proper maintenance is crucial to avoid these issues. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other plant diseases. Choosing plants that thrive in self-watering conditions is important.
It's essential to monitor the moisture levels and adjust watering as needed. Understanding the specific needs of the plants and the planter system is key to successful maintenance.
Can Self-Watering Planters Be Used for All Types of Plants, Including Succulents and Cacti?
When choosing the right plants for self-watering planters, it's important to consider their water needs and adaptability.
Succulents and cacti, known for their low water requirements, can thrive in these planters if proper drainage and soil types are used.
Maintenance tips, like monitoring soil moisture and adjusting watering frequency, are crucial for their well-being.
Understanding the specific needs of different plant types is key to successful cultivation in self-watering planters.
How Often Should the Water Reservoir in a Self-Watering Planter Be Refilled?
We've found that the frequency of refilling the water reservoir in a self-watering planter depends on factors like plant type, size, and environmental conditions.
The benefits of self-watering planters are impressive, akin to a reliable friend who never forgets to water your plants. These systems provide a consistent water supply, reducing the need for frequent refills and ensuring optimal moisture levels for healthy plant growth.
Are There Any Potential Risks or Dangers Associated With Using Self-Watering Planters?
Potential drawbacks of self-watering planters include:
- The risk of overwatering, which can lead to root rot and other water-related issues.
- Concerns about the cost effectiveness and environmental impact of using these planters.
It's essential to carefully monitor the moisture levels and adjust watering frequency accordingly to avoid these potential risks.
Can Self-Watering Planters Be Used in Outdoor Garden Settings, or Are They Better Suited for Indoor Use?
Outdoor versus indoor use of self-watering planters presents unique factors.
Outdoor usage requires consideration of weather elements and drainage. For outdoor settings, select plants that thrive in the specific climate and soil conditions.
Indoor usage offers controlled environments, suitable for a wider range of plant choices.
Balancing these factors ensures optimal plant health and growth.
Are Self-Watering Planters Effective for Keeping Monstera Plants Hydrated?
Yes, a self watering pot for monstera plants can be effective in keeping them hydrated. The built-in water reservoir allows the plant to absorb water as needed, preventing over or under-watering. This can be especially beneficial for monstera plants, which thrive in consistently moist soil.
Conclusion
In conclusion, self-watering planters offer a convenient and efficient way to keep your plants hydrated. By utilizing the principles of capillary action and reservoir systems, these planters provide a consistent water supply for healthy growth.
While there may be some drawbacks, the benefits of self-watering planters make them a viable option for plant care. With proper selection and maintenance, these planters can be a valuable tool for maximizing the health and longevity of your plants.