Trying to keep our plants healthy often puts us in a dilemma between wanting to take care of them and our busy schedules. This is where the convenience of self-watering pots comes in. These containers allow our plants to thrive with minimal effort required from us.
But how exactly do you make one? Well, the process involves a few simple steps and some readily available materials. So, if you're looking for a way to ensure your plants thrive with minimal maintenance, stay tuned to discover the secrets of creating your own self-watering plant pots.
Key Takeaways
- The materials and tools needed for making a self-watering plant pot include plastic containers, wicking material, a platform for support, a drill, and a utility knife.
- The construction of the water reservoir involves drilling holes in the inner planting container, inserting a PVC pipe, attaching an overflow hole in the outer container, and adding a fill tube and screen.
- The wicking system is assembled by choosing a wicking material, cutting it to the appropriate length, threading it through a small hole in the inner planting container's base, and placing it into the outer reservoir filled with soil.
- To set up the self-watering system, the water reservoir should be positioned correctly, the soil wicking mechanism should be established, the wicking material should reach the lower levels of the soil, and the water level should be monitored regularly.
Materials and Tools Needed
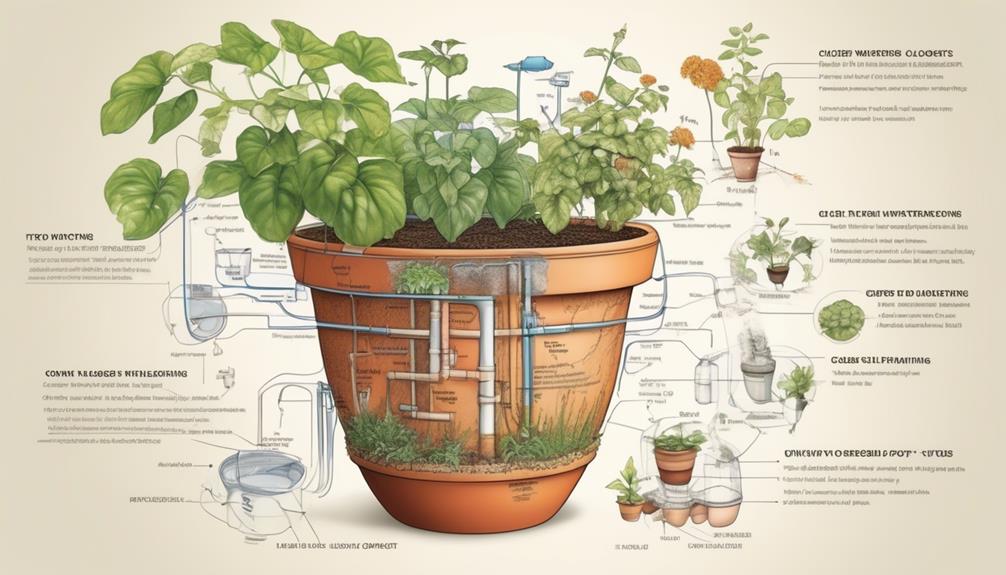
For making self-watering plant pots, we'll need the following materials and tools. First, gather two plastic containers, one larger than the other, to serve as the main pot and reservoir. Additionally, procure a wicking material like cotton rope or felt fabric, which will draw water from the reservoir to the soil. To support the plant and allow for water seepage, obtain a platform such as a small plastic pot or a few bricks. Other essential items include a drill with a small bit for creating a water hole, a utility knife for cutting and shaping the containers, and potting soil suitable for the specific plant being potted.
In sustainable gardening and DIY projects, the choice of materials is crucial to ensure the efficacy of the self-watering system. The wicking material must be absorbent enough to draw water effectively but not rot easily. The containers should be sturdy and durable to support the weight of the plant and withstand moisture. Precision in selecting and assembling these materials is vital for successful implementation of self-watering techniques and optimal plant care.
Constructing the Water Reservoir
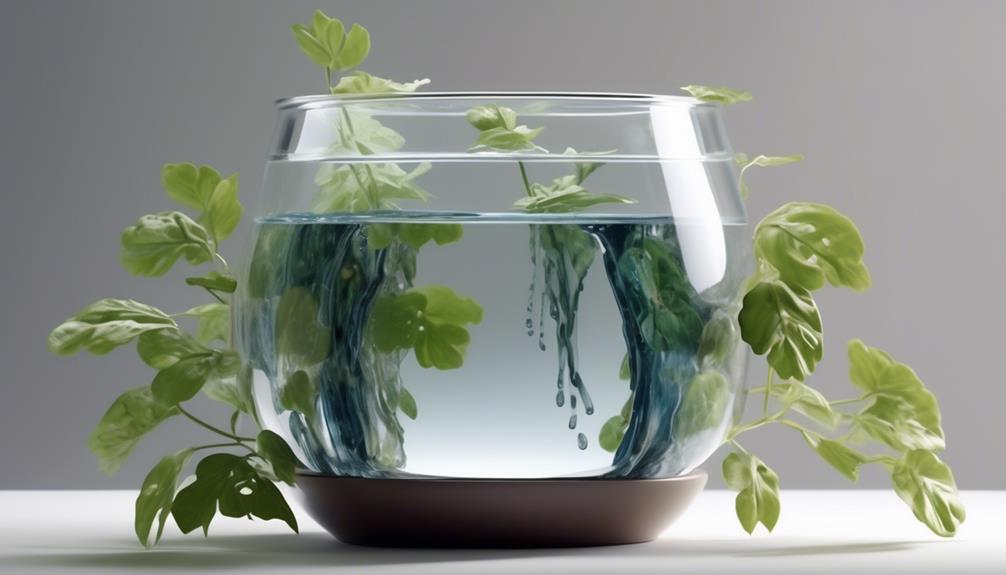

To proceed with constructing the water reservoir, the materials and tools previously mentioned will be utilized in the assembly process. This step is crucial for ensuring watering efficiency and maintaining plant health in self-watering plant pots. Follow these detailed steps to build the water reservoir:
- Drill Holes: Begin by drilling a series of small holes in the bottom of the inner planting container. These holes will allow water to seep through and be stored in the reservoir below.
- Insert Pipe: Next, insert a PVC pipe through the drilled holes, ensuring it extends from the bottom of the inner container to the top of the outer container. This pipe will act as a water fill tube.
- Attach Overflow Hole: Drill a small overflow hole near the top of the outer container to prevent overfilling. Connect this hole to the PVC pipe using a small section of tubing.
- Add Fill Tube and Screen: Place a fill tube into the PVC pipe, and cover the bottom of the inner container with a piece of screen to prevent soil from clogging the reservoir.
- Assemble Containers: Finally, assemble the inner and outer containers, ensuring a snug fit for the reservoir to function effectively.
Following these steps will contribute to successful DIY projects and provide valuable gardening tips for plant enthusiasts seeking to improve watering efficiency and plant health.
Assembling the Wicking System
Using a cotton wick, we'll guide water from the reservoir to the soil in the inner planting container, ensuring consistent moisture for the plants. When choosing a wicking material, it's important to consider options such as nylon rope, felt strips, or even polyester cord. These materials are highly effective at drawing water upward through capillary action.
To assemble the DIY wicking system, cut the selected wicking material to the appropriate length, making sure it reaches from the water reservoir to the bottom of the planting container. Create a small hole in the center of the inner planting container's base and thread the wick through it, ensuring that both ends are accessible.
Place the inner planting container into the outer reservoir, ensuring that the wick hangs down into the water. Then, fill the planting container with soil, making sure to pack it firmly around the wick.
Preparing the Planting Container

After determining the appropriate wicking material and assembling the wicking system, the next step is to prepare the planting container for the self-watering pot. To ensure the successful establishment of your plants, follow these essential steps:
- Planting Depth: Determine the appropriate planting depth for the specific plant species you intend to grow. Different plants require different depths for their roots to thrive, so ensure that the planting container is deep enough to accommodate the root system of your chosen plants.
- Drainage Holes: Check the planting container for drainage holes. If it doesn't have any, consider drilling or punching holes in the bottom of the container to allow excess water to escape. Proper drainage is crucial to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot and other plant health issues.
- Soil Preparation: Before planting, ensure that the soil mix is well-draining and suitable for the plants you intend to grow. It should be a blend of potting soil, perlite, and peat moss to provide the right balance of aeration and moisture retention.
- Fertilizer Placement: Consider the placement of fertilizer in the planting container. Some self-watering pots have a separate compartment for adding liquid fertilizer, which can enhance plant growth and health.
- Mulching: Apply a layer of mulch on top of the soil to help retain moisture and regulate soil temperature, promoting optimal growing conditions for your plants.
Setting Up the Self-Watering System
First, we'll set up the water reservoir, ensuring it's positioned correctly to provide consistent moisture to the plant.
Next, we'll establish the soil wicking mechanism, which will draw water from the reservoir to the plant's roots.
Water Reservoir Setup
to the plant roots
This setup will help maintain proper plant care and ensure an effective irrigation system.
Soil Wicking Mechanism
Setting up the self-watering system's soil wicking mechanism involves seamlessly integrating the water reservoir, ensuring a steady supply of moisture to the plant roots through a carefully constructed fabric or rope system. This mechanism is crucial for watering efficiency and root health.
The fabric or rope extends from the water reservoir into the soil, allowing water to be drawn upward through capillary action, preventing evaporation and ensuring continuous moisture for the roots. This method not only prevents overwatering but also promotes nutrient absorption, creating an ideal environment for plant growth.
The wicking material should be placed in a way that it reaches the lower levels of the soil where the plant roots reside, optimizing the water distribution for the plant's overall well-being.
Proper installation and maintenance of the soil wicking mechanism are essential for the long-term success of the self-watering system.
Monitoring Water Level
Monitoring the water level in the self-watering system is essential for ensuring consistent and adequate moisture for the plants.
To effectively monitor the water level, the following steps are crucial:
- Set a watering schedule based on the specific needs of the plants to maintain optimal moisture levels.
- Use a moisture sensor to accurately measure the moisture content in the soil and integrate technology for automated monitoring.
- Regularly check the water level indicator to ensure that an adequate supply of water is available for the plants.
- Adjust the watering schedule based on the plant's health and environmental conditions to prevent over or under-watering.
- Implement a reliable and efficient system for tracking and managing the water level to ensure the overall health and vitality of the plants.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting
Now that we've set up the self-watering system, it's crucial to maintain the proper watering frequency and monitor the soil moisture level.
By understanding the water needs of different plant species and adjusting the watering schedule accordingly, we can ensure optimal growth and health.
Additionally, troubleshooting any issues with clogging or water flow will be essential to keep the self-watering pots functioning effectively.
Watering Frequency
When determining the watering frequency for your self-watering plant pots, consider the specific needs of the plant species being grown and the environmental conditions in which they're situated. Factors such as the plant's size, growth stage, and water requirements play a crucial role in determining the frequency of watering. Additionally, climate, temperature, and humidity levels also impact the rate at which the plant consumes water.
To ensure optimal plant growth and water conservation, follow these guidelines:
- Monitor the soil moisture regularly to assess the watering needs accurately.
- Adjust the watering frequency based on seasonal changes in temperature and humidity.
- Use a water meter to gauge the moisture levels in the soil.
- Consider the specific water requirements of different plant species in your self-watering pots.
- Be mindful of overwatering, as it can lead to root rot and other plant health issues.
Soil Moisture Level
Maintaining the appropriate soil moisture level is essential to the health and growth of plants in self-watering pots. It directly correlates with the watering frequency discussed earlier.
Achieving optimal soil moisture is crucial for plant growth. The soil should be consistently moist but not waterlogged. To maintain this balance, it's important to monitor the water retention capability of the soil mix.
If the soil becomes too dry, it can hinder plant growth, while excessively wet soil can lead to root rot. To troubleshoot, check the soil moisture by feeling it with your fingers or using a soil moisture meter. Adjust the watering frequency accordingly.
Additionally, consider using a well-draining soil mix to ensure proper water retention and prevent waterlogging. This will ultimately promote healthy plant growth in self-watering pots.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Use a Self-Watering Pot for Any Type of Plant, or Are There Specific Plants That Work Best With This System?
We've found that not all plants are suitable for self-watering pots. It's best to use plants that thrive in consistently moist soil, such as ferns, peace lilies, and snake plants. These plants are well-suited for the self-watering system and will benefit from it.
It's important to consider the watering needs of the specific plant and adjust the self-watering pot accordingly. Following these tips will ensure the best results with your self-watering system.
How Often Do I Need to Refill the Water Reservoir in a Self-Watering Pot?
We should check and refill the water reservoir in a self-watering pot every 1-2 weeks, depending on the plant's water needs and environmental conditions.
It's crucial to monitor the soil moisture and adjust the watering schedule accordingly.
The potting mix and soil type also play a role in determining the frequency of refilling.
With a proper understanding of these factors, we can ensure an ideal watering regimen for our plants.
Can I Use Any Type of Soil in a Self-Watering Pot, or Are There Specific Types That Work Best With This System?
We've found that self-watering pots work best with well-draining soil mixes like peat-based or coir-based blends. These soils allow the water to move freely through the reservoir and into the root zone. It's important to avoid using heavy soils or those with high clay content as they can impede water flow.
When it comes to watering frequency, the soil type can impact how often you need to refill the reservoir.
Are There Any Potential Drawbacks or Downsides to Using a Self-Watering Pot for My Plants?
Potential drawbacks of self-watering pots include maintenance requirements, as they can clog or grow algae. However, their cost effectiveness and environmental impact make them a worthwhile investment.
It's important to regularly clean and check the water levels to ensure optimal plant growth. These pots are like a double-edged sword, offering convenience but requiring attention to detail for long-term success.
How Can I Tell if My Self-Watering Pot Is Not Working Properly, and What Can I Do to Troubleshoot Any Issues?
If the self-watering pot isn't working, signs like dry soil or wilting plants may occur. To troubleshoot, check if the water reservoir is empty, or the wick is clogged. Clean the wick, refill the reservoir, or adjust the water level.
Ensure the drainage holes aren't blocked. Regular maintenance prevents issues. Clean the pot and wick, and check for proper water flow.
These troubleshooting tips and maintenance help keep the self-watering pot working effectively.
Can self watering pots be used for all types of plants?
Yes, planting in self watering pots can be suitable for a wide variety of plants, including indoor and outdoor varieties. However, it’s important to consider the specific water needs of each plant, as some may require more or less water than others. Overall, self watering pots can provide a convenient and effective way to keep your plants hydrated.
Conclusion
In conclusion, creating a self-watering plant pot is a great way to ensure your plants are getting the water they need without constant monitoring.
It's a real game-changer for us busy plant parents.
So, grab your materials and get ready to make your very own self-watering plant pots – you won't regret it!










