Are you ever so busy with tasks that you forget to take care of your plants? Self-watering planters might be the solution you need. These innovative containers eliminate the guesswork of watering by providing a consistent water supply to your plants.
But how exactly do they work? Let's uncover the fascinating science behind self-watering planters and explore the benefits they offer to both novice and experienced gardeners alike.
Key Takeaways
- Self-watering planters utilize a reservoir and wicking system to provide consistent moisture supply to plants.
- Capillary action is a key process for water movement in self-watering planters, facilitated by the reservoir.
- Self-watering planters regulate soil moisture effectively, reducing the risk of over or underwatering.
- The wicking system in self-watering planters mimics the natural way plants draw water from the soil, preventing water stagnation and allowing roots to access water.
Self-Watering Planter Basics
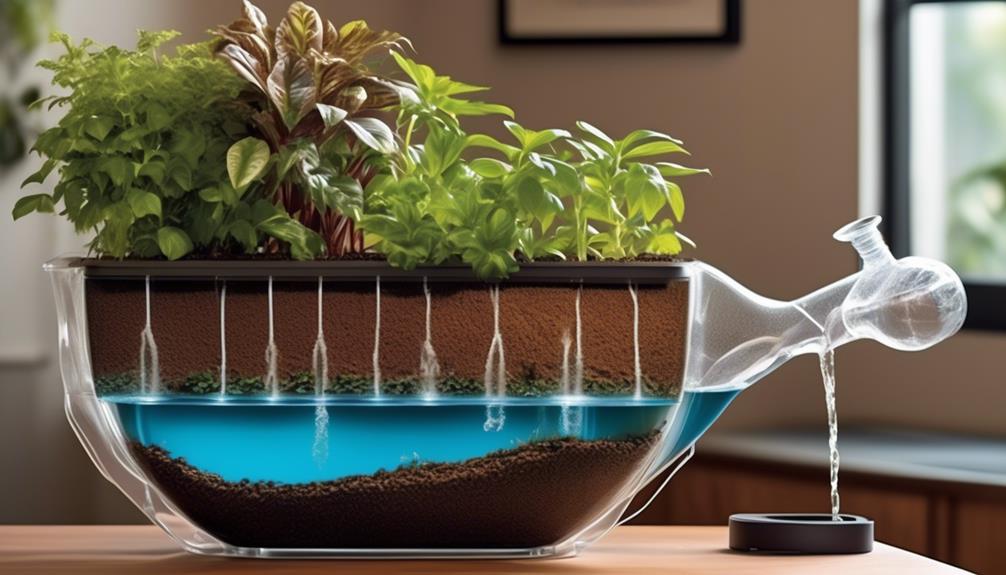
Self-watering planters are designed to provide a consistent supply of moisture to plants by utilizing a reservoir and a wicking system to deliver water directly to the roots as needed. This innovative design ensures optimal plant hydration by mimicking natural watering conditions.
The planter design typically includes a water reservoir at the bottom, separated from the soil by a platform or wicking system. This reservoir stores water, which is then drawn up into the soil through capillary action, keeping the soil consistently moist.
The wicking system, often made of a porous material like fabric or a special wick, allows water to move from the reservoir into the soil, maintaining an ideal level of moisture for the plants. This process effectively prevents overwatering or underwatering, as the plants can draw water as needed. The planter design also usually includes a water level indicator, which allows for easy monitoring of the water reservoir, ensuring that the plants have an adequate water supply.
Understanding the basics of self-watering planters is crucial for mastering plant hydration and optimizing growth. By comprehending the planter design and the mechanisms behind it, plant enthusiasts can achieve healthier and more vibrant greenery.
Capillary Action Principle

Capillary action is the key process by which water moves from the reservoir into the soil in self-watering planters, ensuring consistent and efficient moisture delivery to the plant roots.
This principle relies on the ability of water to move through narrow spaces, such as the small channels within the soil.
As the soil in the planter dries out, the water in the reservoir below is drawn upwards through the soil via capillary action.
This upward movement continues until the soil reaches a state of equilibrium with the water in the reservoir, ensuring that the plant roots have access to water as needed.
The capillary action principle plays a critical role in maintaining watering efficiency and sustaining plant health in self-watering planters.
By allowing the soil to draw up water as required, this process prevents overwatering and underwatering, ultimately promoting optimal conditions for plant growth.
Understanding and harnessing capillary action is fundamental to the successful functioning of self-watering planters, ensuring that plants receive consistent and adequate moisture for their well-being.
Reservoir Function
When it comes to the reservoir function of self-watering planters, it's crucial to understand the water absorption mechanism, which allows the soil to draw water from the reservoir as needed.
This process is facilitated by the capillary action, which enables the water to move upward through the soil, ensuring consistent moisture levels.
Water Absorption Mechanism
Using a porous material such as soil or a specialized wicking material, water is drawn up from the reservoir of a self-watering planter through capillary action to provide consistent moisture to the plant's roots.
The water absorption mechanism in self-watering planters operates with remarkable efficiency, ensuring optimal plant hydration. When the soil or wicking material comes into contact with the water reservoir, it begins to absorb the water through capillary action, similar to how a sponge soaks up liquid.
This absorbed water then moves upwards, defying gravity, to reach the plant's roots, maintaining a balanced level of moisture. As the plant draws water as needed, the reservoir automatically and gradually refills, creating a self-sustaining cycle of hydration for the plant.
This mechanism significantly reduces the frequency of manual watering while promoting healthier and more vibrant plant growth.
Capillary Action Process
The efficient water absorption mechanism discussed previously seamlessly integrates with the capillary action process, specifically focusing on the reservoir function in self-watering planters.
Capillary action, driven by cohesive and adhesive forces, allows water to move from the reservoir to the soil. When the soil becomes dry, it creates a negative water potential, prompting water from the reservoir to move upwards through small spaces in the soil via capillary action. This ensures a consistent moisture level in the soil, promoting optimal watering efficiency.
Soil Moisture Regulation
To regulate soil moisture effectively, self-watering planters utilize a reservoir that facilitates capillary action, ensuring a consistent supply of water to the plant's roots.
The reservoir functions by:
- Drawing water from the reservoir up into the soil through capillary action, mimicking the plant's natural hydration process.
- This capillary action is driven by the attraction of water to the soil particles and the plant's roots, allowing for efficient soil moisture management.
- As the soil dries out, the capillary action pulls more water from the reservoir, maintaining optimal moisture levels for the plant's hydration.
This soil moisture regulation is crucial for the overall health of the plant, as it ensures a constant supply of water, promoting healthy growth and reducing the risk of over or underwatering.
Wicking System Explanation
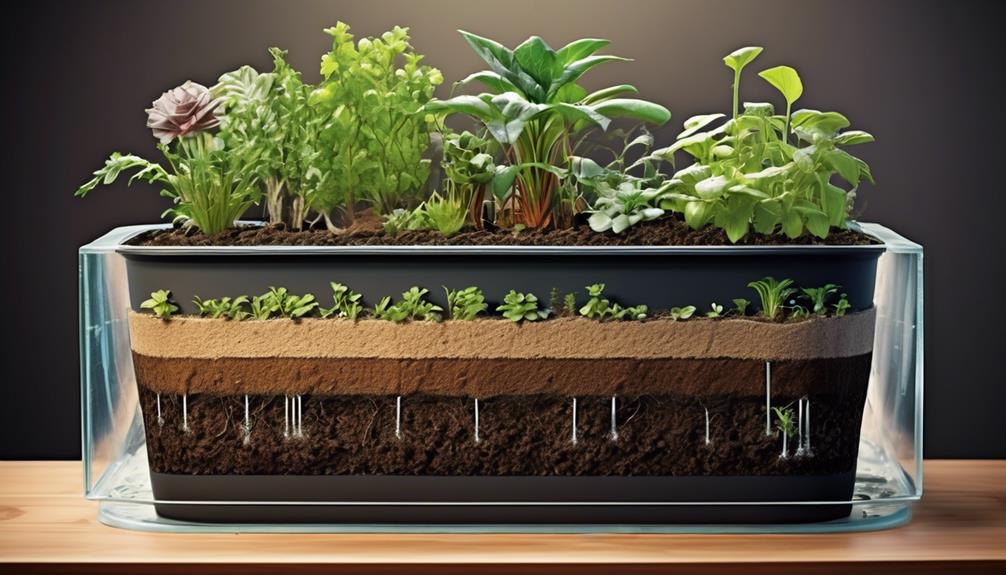

The wicking system in self-watering planters is a crucial component that allows for the efficient distribution of water to the plant's roots. This process relies on capillary action, where water moves upwards through a porous material, such as soil or a wick, due to the forces of adhesion and cohesion.
Understanding the wicking process is essential for optimizing the functionality of self-watering planters and ensuring that plants receive the appropriate moisture levels for healthy growth.
Wicking Process
By utilizing capillary action, the wicking process in self-watering planters draws water from the reservoir into the soil, providing consistent moisture to the plant's roots. This process ensures watering efficiency by preventing water stagnation and allowing the roots to access water as needed.
The wicking system also promotes optimal plant growth by maintaining a balanced moisture level, preventing both overwatering and underwatering. Through capillary action, the water travels upwards through the soil, reaching the plant's root zone uniformly.
As the soil dries out, the wicking process continues to supply moisture, creating an ideal environment for the roots to absorb water and nutrients. The capillary action of the wicking process mimics the natural way in which plants draw water from the soil, fostering healthy and vigorous growth.
Capillary Action
Utilizing capillary action, our self-watering planters employ a wicking system that draws water from the reservoir into the soil, ensuring consistent moisture for the plant's roots. Capillary action, also known as capillarity, is the ability of a liquid to flow in narrow spaces without the assistance of, or even in opposition to, external forces like gravity. In our self-watering planters, this capillary action allows water to move upwards from the reservoir into the soil, keeping it consistently moist. This wicking system enhances watering efficiency by delivering water directly to the plant's roots as needed, promoting optimal plant health. Below is a table illustrating how capillary action works in our self-watering planters:
| Capillary Action in Self-Watering Planters |
|---|
| Utilizes capillarity to draw water from reservoir |
| Moves water upwards into soil |
| Ensures consistent moisture for plant's roots |
This mechanism ultimately contributes to the overall health and vitality of the plants.
Soil Moisture Regulation
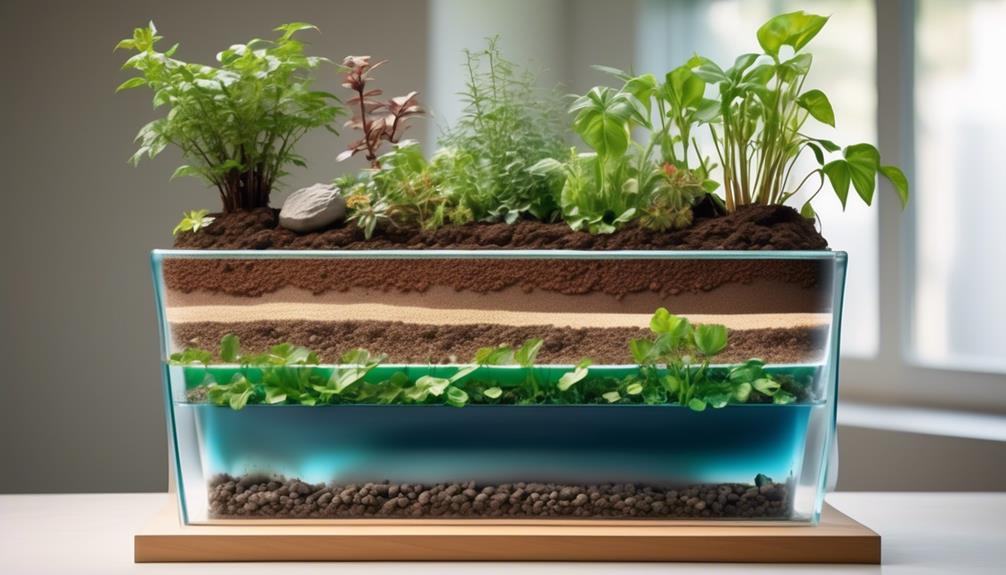

Maintaining optimal soil moisture is essential for the health and growth of plants in self-watering planters. In these planters, soil moisture regulation is achieved through a combination of irrigation efficiency and water conservation techniques.
Firstly, the self-watering system utilizes a wicking mechanism to efficiently draw water from the reservoir into the soil. This capillary action ensures that the roots have access to water as needed, promoting healthy plant growth.
The soil moisture is carefully monitored and regulated through the use of a water level indicator, which prevents overwatering or underwatering. This precise regulation ensures that the plants receive the perfect amount of moisture, promoting optimal growth and vitality.
Additionally, the design of the planter includes aeration features that prevent waterlogging and promote oxygen circulation in the soil, further enhancing the plant's health and vigor.
Root Hydration Process
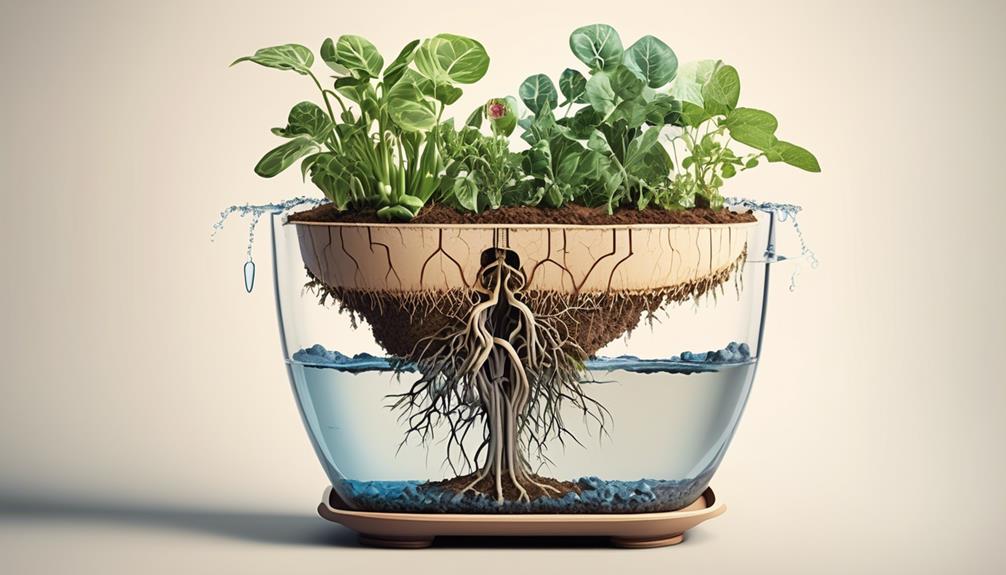

When it comes to the root hydration process in self-watering planters, understanding the water absorption process and soil moisture regulation is crucial.
The roots of the plants play a vital role in absorbing water from the reservoir and distributing it to the rest of the plant.
Water Absorption Process
The process of water absorption in plants involves the intricate coordination of root structures, cellular osmosis, and nutrient transport mechanisms.
- As water enters the root system, it moves through the apoplast—a network of cell walls and intercellular spaces—aided by capillary action, allowing for a more efficient uptake of water and nutrients.
- Once inside the roots, water moves through the symplast, crossing cell membranes via osmosis, ensuring that each cell receives the necessary hydration for optimal function and growth.
- The Casparian strip, a waterproof barrier in the root endodermis, promotes sustainable gardening and water conservation by regulating the passage of water and nutrients into the vascular system, thus enhancing watering efficiency and ultimately supporting healthy plant growth.
Soil Moisture Regulation
After water enters the root system and moves through the apoplast and symplast, the process of regulating soil moisture becomes essential for sustaining optimal root hydration and supporting healthy plant growth.
Soil moisture management involves intricate mechanisms within the plant that ensure water is available to the roots when needed. One vital aspect of this regulation is the control of stomatal openings on the leaves, which is crucial in preventing excessive water loss through transpiration while facilitating gas exchange.
Additionally, plant hydration techniques such as the secretion of abscisic acid in response to water stress play a pivotal role in modulating the plant's water uptake and loss.
Understanding these processes is fundamental for maintaining the right balance of soil moisture, enabling plants to thrive in various environmental conditions.
Evaporation Prevention Mechanism

To minimize water loss through evaporation, self-watering planters utilize a unique mechanism that ensures efficient moisture retention within the soil. This evaporation prevention mechanism is crucial for maintaining optimal soil moisture levels and promoting plant hydration.
The following details how this mechanism works:
- Capillary Action: The self-watering planter is designed with a capillary wick system that draws water from the reservoir into the soil through capillary action. This ensures that the soil remains consistently moist without excessive water exposure to the air, thus minimizing evaporation.
- Aeration Control: The planter incorporates aeration mechanisms that allow oxygen to reach the roots while minimizing the escape of moisture-laden air. This helps in preventing excessive evaporation while maintaining a healthy root environment.
- Covering and Insulation: Many self-watering planters are equipped with covers or insulating materials that reduce direct exposure of the soil to air, thereby decreasing evaporation rates and enhancing water retention within the planter.
The evaporation prevention mechanism in self-watering planters not only controls evaporation but also plays a vital role in maintaining moisture regulation, promoting plant hydration, and ensuring the overall health of the plants.
Ideal Plant Selection

When selecting plants for self-watering planters, we need to consider their specific water needs, soil moisture requirements, and root system characteristics.
Certain plants require more water than others, so it's important to match their water needs with the self-watering planter's capabilities.
Additionally, understanding the moisture levels preferred by different plant species and their root system requirements is crucial for successful growth in self-watering planters.
Plant Water Needs
Selecting the ideal plant for a self-watering planter involves considering the specific water needs of the plant species to ensure proper hydration and growth. When choosing plants for self-watering planters, it's crucial to consider their water absorption capabilities, as different species have varying requirements. Here's what to consider:
- Plant Hydration: Some plants require consistently moist soil to thrive, while others prefer periods of dryness between watering. Understanding the hydration needs of the plant is essential.
- *Water Absorption*: Plants with high water absorption, such as peace lilies, ferns, and certain types of palms, are well-suited for self-watering planters as they can draw water from the reservoir as needed.
- *Water Retention*: Succulents and cacti are ideal for self-watering planters with well-draining soil, as they store water in their leaves and stems, making them tolerant of infrequent watering.
Selecting the right plant based on its water needs ensures a flourishing and healthy indoor garden.
Soil Moisture Levels
Considering the optimal soil moisture levels is crucial when selecting plants for self-watering planters, as it directly impacts their growth and overall health. Different plants have varying irrigation techniques and moisture retention capabilities.
For example, plants like succulents and cacti prefer drier soil and benefit from infrequent watering. On the other hand, plants such as ferns and peace lilies thrive in consistently moist soil.
When choosing plants for self-watering planters, it's essential to match their moisture requirements with the planter's capabilities. Self-watering planters are designed to maintain consistent moisture levels, making them suitable for a wide range of plants.
Understanding the moisture needs of different plant species allows for informed decisions, ensuring the plants not only survive but thrive in self-watering planters.
Root System Requirements
Understanding the specific root system requirements of different plant species is essential for successful plant selection in self-watering planters. When choosing plants for self-watering containers, it's crucial to consider their root system development, as it directly impacts water uptake efficiency. Here are some key considerations for ideal plant selection:
- Shallow Rooted Plants: Select plants with shallow root systems, such as herbs like basil and thyme, which thrive in self-watering planters.
- Visualize: Imagine delicate, fibrous roots spreading horizontally just below the soil surface, efficiently absorbing water and nutrients.
- Compact Root Systems: Opt for plants with compact root systems, like dwarf varieties of vegetables or ornamental flowers, to ensure efficient water uptake.
- Imagery: Envision dense, clustered roots that efficiently take up water and support the plant's water needs.
- Adapted Varieties: Choose plants that are adapted to container gardening, such as compact fruit varieties or dwarf shrubs, ensuring their root systems can effectively utilize the self-watering planter's design.
- Visualization: Picture root systems optimized for efficient water absorption and utilization within the confined space of the planter.
Watering Frequency Control
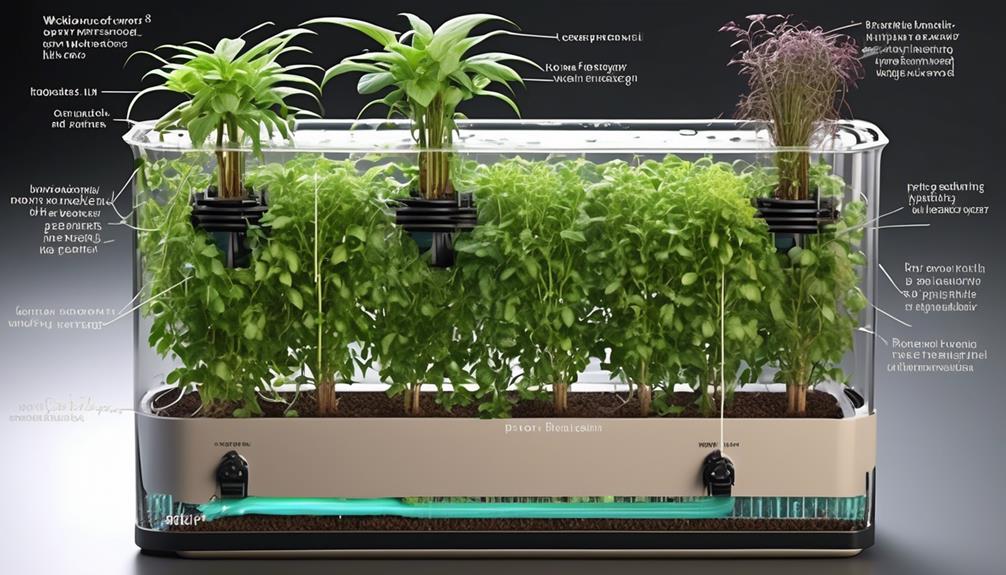

Controlling the watering frequency in self-watering planters is essential for maintaining optimal moisture levels for the plants' health and growth. A well-managed watering schedule is crucial for plant health as it ensures that the roots receive consistent moisture, preventing issues such as overwatering or underwatering. Monitoring the moisture level is key to promoting healthy plant growth.
By adjusting the watering frequency based on the specific needs of the plant and the environmental conditions, we can create an ideal balance that supports robust root development and overall plant vitality.
When establishing a watering schedule, factors such as the plant species, size of the planter, and ambient humidity levels must be considered. For example, plants in larger containers may require less frequent watering than those in smaller ones due to the increased soil volume. Furthermore, understanding the water requirements of different plants is essential for tailoring the watering frequency to their specific needs.
Overwatering Prevention

To prevent overwatering in self-watering planters, we carefully monitor the soil moisture levels and adjust the watering frequency as needed. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other issues that can harm plant root health, so it's crucial to maintain a balance. Here's how we prevent overwatering:
- Moisture Retention: We utilize a well-designed soil mix that provides proper aeration and moisture retention, ensuring that excess water doesn't accumulate around the roots.
- *Soil Composition*: Our soil mix includes materials like perlite or vermiculite, which improve drainage and prevent waterlogged conditions.
- *Capillary Action*: The planter's wicking system uses capillary action to deliver water to the roots as needed, preventing water from pooling at the bottom of the container.
- Watering Efficiency: We optimize the watering system to deliver just the right amount of water to the plant, reducing the risk of overwatering.
- *Monitoring Tools*: We utilize moisture meters or sensors to gauge the soil moisture levels accurately, allowing us to adjust the watering frequency with precision.
- *Adaptive Control*: Some self-watering systems are equipped with features that adjust water flow based on environmental conditions, further preventing overwatering.
Nutrient Distribution Method

Utilizing a gravity-fed system, the nutrient distribution method in self-watering planters ensures a consistent supply of essential nutrients to the plant roots. As water is drawn up from the reservoir through capillary action, it carries dissolved nutrients along, delivering them directly to the root zone. This method optimizes nutrient absorption by maintaining a moist yet well-aerated environment around the roots, allowing for efficient uptake of essential elements.
The design of the self-watering planter also promotes effective water retention, further enhancing the nutrient distribution process. By utilizing a water reservoir at the bottom of the planter, the system ensures that the soil remains consistently moist without becoming waterlogged. This constant moisture level supports the roots' ability to uptake nutrients, as it prevents fluctuations in soil moisture that can hinder nutrient absorption.
Additionally, the consistent moisture level fosters beneficial microbial activity in the soil, further enhancing nutrient availability to the plants.
Aeration and Oxygen Supply

In self-watering planters, maintaining adequate aeration and oxygen supply is crucial for promoting healthy root development and overall plant growth. The oxygenation process in these planters is facilitated by an aeration mechanism that ensures the roots receive the necessary oxygen for cellular respiration. This oxygen supply technique is essential for preventing root rot and promoting nutrient uptake, leading to robust and thriving plants.
To achieve this, self-watering planters commonly employ the following methods:
- Aeration Mechanism: The planter design incorporates aeration mechanisms such as air vents or porous materials that allow oxygen to enter the root zone and carbon dioxide to exit, simulating natural soil conditions.
- Root Oxygenation: The planter's self-regulating water reservoir helps in maintaining optimal moisture levels, preventing waterlogging, and ensuring the roots have access to oxygen, promoting healthy root growth.
- Oxygen Supply Technique: Utilizing capillary action, the soil wicks up water from the reservoir, carrying oxygen to the roots and facilitating gas exchange, creating an ideal environment for root development and overall plant health.
Planter Material Impact

The choice of planter material significantly impacts the aeration, moisture retention, and overall functionality of self-watering planters. When comparing planter materials, it's essential to consider their properties and how they affect plant growth.
Porous materials like terracotta allow for good aeration and moisture evaporation, which can be beneficial for some plants but may require more frequent watering. On the other hand, plastic or resin-based planters offer better moisture retention, reducing the watering frequency. However, they may not provide the same level of aeration as porous materials.
Additionally, environmental impact considerations should guide the choice of planter material. Reusable and recyclable materials, such as food-grade plastics or sustainably sourced wood, are more environmentally friendly options.
Understanding the specific needs of the plants and the environmental impact of the chosen materials is crucial when selecting the right planter for a self-watering system. By carefully evaluating these factors, one can maximize the effectiveness of self-watering planters while minimizing their environmental footprint.
Maintenance Tips and Tricks

Regularly inspecting the water level and cleanliness of the reservoir, as well as cleaning the watering mechanism, is essential for maintaining the optimal functionality of self-watering planters.
To ensure the proper maintenance of self-watering planters, consider the following tips and tricks:
- Watering Schedule:
- Monitor the water level in the reservoir at least once a week to ensure it doesn't run dry, especially during hot weather when plants may require more water.
- Adjust the watering frequency based on the type of plants and their individual water needs. For example, plants in self-watering planters may require watering less frequently compared to those in traditional pots.
- Soil Testing:
- Periodically check the moisture level of the soil in the planter to ensure it remains within the ideal range for the specific plant species.
- Use a soil moisture meter to gauge the moisture content accurately and avoid overwatering or underwatering the plants.
- Cleaning and Maintenance:
- Regularly clean the watering mechanism to prevent clogging and ensure a steady flow of water to the plants.
- Inspect the planter for any signs of algae, mold, or mineral deposits, and clean the reservoir and planter surface accordingly to maintain a healthy growing environment.
Benefits for Busy Gardeners
Monitoring the water level and soil moisture in self-watering planters is crucial for busy gardeners, allowing us to ensure our plants receive the proper care even during hectic schedules. The benefits of self-watering planters are particularly valuable for those of us with limited time to dedicate to gardening. These time-saving techniques not only help us maintain healthy and thriving plants, but also increase our overall gardening efficiency.
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Water Conservation | Self-watering planters minimize water wastage by delivering water directly to the plant roots. |
| Reduced Maintenance | These planters require less frequent watering, saving us time and effort in the long run. |
| Enhanced Plant Growth | Consistent moisture levels lead to improved plant growth, resulting in healthier and lush foliage. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Self-Watering Planters Be Used for All Types of Plants, Including Succulents and Cacti?
Yes, self-watering planters can be used for all types of plants, including succulents and cacti.
When it comes to succulent care, it's essential to control the watering frequency. Self-watering planters provide a consistent moisture level, which is ideal for succulents that require infrequent watering.
The planters prevent overwatering and help maintain the proper soil moisture for succulents and cacti to thrive.
Are There Any Special Considerations for Using Self-Watering Planters in Hot or Dry Climates?
Are there any special considerations for using self-watering planters in hot or dry climates?
In hot or dry climates, special attention should be given to watering frequency, soil type, and container size. The watering techniques and plant health may need to be adjusted to accommodate the environmental conditions.
It's crucial to choose the right soil mix and container size to ensure optimal moisture retention and plant growth in these challenging climates.
What Are the Potential Drawbacks or Limitations of Self-Watering Planters Compared to Traditional Watering Methods?
When considering the limitations of self-watering planters compared to traditional watering methods, it's important to assess their effectiveness and efficiency.
Drawbacks may include potential clogging of the watering system, leading to uneven water distribution.
Additionally, some plants may have specific water needs that aren't easily met by self-watering systems.
Understanding these limitations can help us optimize the effectiveness of self-watering planters while addressing their drawbacks.
How Do Self-Watering Planters Impact the Overall Water Consumption and Conservation in a Garden or Indoor Space?
In our experience, self-watering planters have significantly impacted water consumption and conservation in our garden and indoor spaces. They've improved water efficiency, ensuring optimal moisture levels for plant growth.
Particularly beneficial in urban environments, they reduce water wastage and maintenance. Compared to traditional methods, they offer consistent hydration and lower water usage.
To maintain them in different climates and seasons, we recommend adjusting watering frequency and monitoring soil moisture levels.
Are There Any Specific Maintenance Tasks or Adjustments Required for Self-Watering Planters During Different Seasons or Weather Conditions?
Seasonal adjustments and weather maintenance are crucial for the optimal functioning of self-watering planters.
In different seasons, we adjust watering frequency and monitor soil moisture levels. During hot weather, we ensure that the reservoir is filled more frequently to prevent the soil from drying out. Conversely, in colder weather, we reduce watering to prevent waterlogging.
Regularly checking the planter's drainage and adjusting accordingly is essential for plant health and growth.
How Does the Self Watering Mechanism in the Flare Planter Work?
The self watering planter option in the Flare Planter works by utilizing a reservoir at the bottom. The soil wicks up the water to hydrate the plant roots as needed. This mechanism ensures consistent moisture levels, reducing the frequency of watering and helping plants thrive.
Conclusion
In conclusion, self-watering planters utilize the capillary action principle to draw water from a reservoir into the soil, keeping plants hydrated for longer periods. The wicking system ensures even moisture distribution, while the planter material impacts the overall effectiveness.
With proper maintenance and regular monitoring, these planters can be a game-changer for busy gardeners, allowing them to have their plants 'on autopilot' while they focus on other tasks.
So, why not give self-watering planters a try and simplify your gardening routine?










