We have reached a point where acknowledging the truth is crucial – self-watering planters have revolutionized gardening for many fans. However, this raises the question: are we overstating the advantages of these planters? It is commonly known that there are always two sides to every story.
When it comes to self-watering pots, the debate over their benefits and drawbacks is ongoing. Whether they are a blessing or a curse for your leafy companions is a question worth exploring.
So, let's dive into the world of self-watering pots and unravel the complexities that surround them.
Key Takeaways
- Self-watering pots provide a consistent and efficient method for delivering water to plants.
- They promote healthy growth by reducing the risk of over or under-watering.
- Self-watering pots help conserve water by reducing evaporation and runoff.
- They support robust root development and overall plant health.
Benefits of Self-Watering Pots
Self-watering pots provide a consistent and efficient method for delivering water to plants, promoting healthy growth and reducing the risk of over or under-watering. These pots are designed with a reservoir at the bottom, which holds excess water that can be drawn up into the soil as needed. This mechanism not only benefits the plants but also offers water conservation benefits by reducing water wastage through evaporation or runoff. The self-watering feature ensures that the plants receive a steady supply of water, preventing the soil from drying out and the plants from becoming stressed due to inadequate hydration.
Furthermore, the consistent moisture levels achieved through self-watering pots contribute to plant growth optimization. By maintaining an ideal balance of moisture in the soil, the pots support robust root development and overall plant health. This is especially beneficial for delicate or thirsty plants that require precise watering schedules. The regulated hydration also minimizes the occurrence of water-related issues such as root rot or wilting, ultimately fostering optimal conditions for plant growth.
How Self-Watering Pots Work
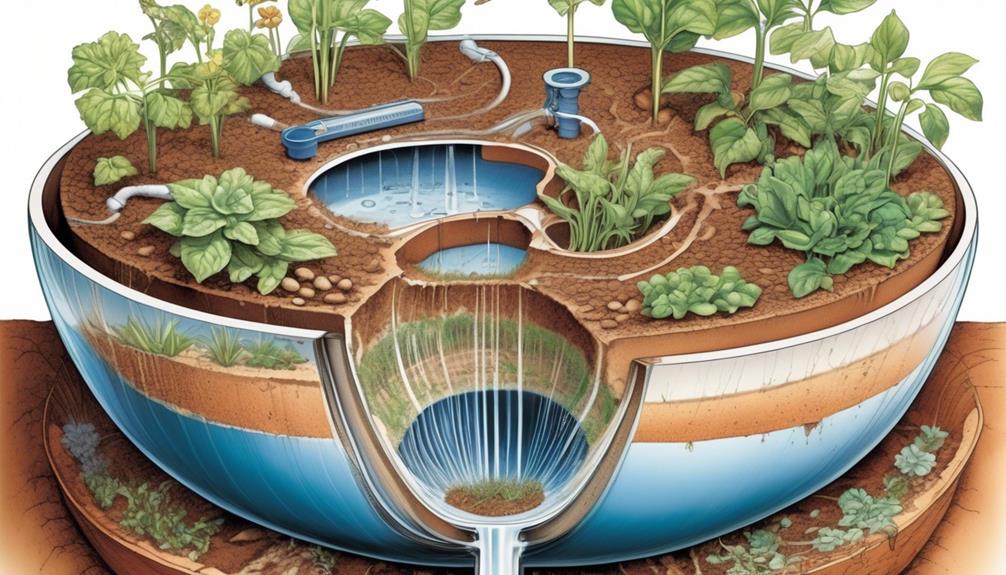
Self-watering pots operate through a wicking system that draws water from a reservoir into the soil, providing consistent moisture to the plant. This mechanism offers the benefit of reducing the frequency of watering and helps prevent overwatering, which can be detrimental to plant health.
However, potential drawbacks include the risk of water stagnation and the need for periodic maintenance to ensure proper functioning.
Self-Watering Pot Mechanism
How does the mechanism of self-watering pots function to provide a consistent and controlled water supply to plants without the need for frequent manual watering?
Self-watering pots operate on the principle of capillary action and gravity. The pot is divided into two chambers, one for the plant and soil, and the other for water storage. A wick or porous material extends from the water reservoir into the soil, allowing water to move upward through capillary action, ensuring consistent soil moisture levels.
As the soil moisture decreases, the plant roots draw water through the wick, maintaining optimal hydration. This mechanism reduces the watering frequency by providing a steady supply of water to the plant as needed.
Benefits of Self-Watering
The mechanism of self-watering pots effectively maintains consistent soil moisture levels, promoting healthy plant growth while reducing the need for frequent manual watering. This system operates through a reservoir that holds water, which is gradually absorbed by the soil through capillary action. As a result, the plants receive a consistent water supply, ensuring optimal hydration without the risk of overwatering or underwatering.
This watering efficiency not only saves time but also promotes plant health by preventing water stress and root suffocation. Additionally, the self-watering mechanism reduces the frequency of manual watering, making it an ideal solution for individuals with busy schedules or those who may forget to water their plants regularly.
Potential Drawbacks
While self-watering pots offer numerous benefits, it's important to consider potential drawbacks in how these pots work to maintain a balanced perspective on their overall effectiveness.
When using self-watering pots, there are some potential risks to consider that may impact plant health:
- Overwatering: The self-watering system can lead to overwatering if not properly monitored, which can cause root rot and other water-related issues.
- Nutrient Buildup: The continuous water supply in self-watering pots can lead to a buildup of nutrients in the soil, potentially causing nutrient imbalances for the plants.
- Algae Growth: The moist environment created by the self-watering system can promote algae growth, which may compete with the plants for nutrients and impact their health.
- Root Restriction: In some self-watering pots, the design may lead to restricted root growth, affecting the overall health and development of the plants.
Potential Risks for Plants

Using a self-watering pot may lead to overwatering, which can result in root rot and other detrimental effects on plant health. The self-watering mechanism can make it challenging to control the amount of water the plant receives, potentially leading to waterlogged soil and reduced oxygen availability to the roots. This can impede plant hydration and nutrient uptake, ultimately affecting the plant's growth potential. Moreover, the soil composition in self-watering pots may be prone to compacting, further exacerbating drainage issues. To illustrate the potential risks for plants, the following table outlines the key factors to consider when using self-watering pots:
| Factors | Implications |
|---|---|
| Watering frequency | Difficulty in regulating water intake may lead to overwatering. |
| Soil composition | Compacting of soil can hinder drainage, causing waterlogged conditions. |
To mitigate these risks, careful monitoring of the soil moisture and adjusting the watering frequency is essential. Additionally, using a well-draining, lightweight soil mix specifically designed for self-watering containers can help maintain optimal soil conditions. Understanding these potential risks is crucial for effectively utilizing self-watering pots while safeguarding plant health.
Types of Self-Watering Systems

In the realm of self-watering systems, there are several types that cater to different plant needs.
The passive wick system utilizes a wick that draws water from a reservoir to the soil.
Capillary action pots rely on the natural movement of water through porous materials to keep the soil moist.
Reservoir planters have a separate compartment for water, allowing the plant roots to absorb moisture as needed.
Passive Wick System
The passive wick system is a self-watering technique commonly utilized in plant containers to maintain consistent soil moisture levels. This system works by using a wick, such as a piece of fabric or rope, to draw water from a reservoir into the soil.
Here are key points about the passive wick system:
- Capillary Action: The wick absorbs water from the reservoir and transports it to the soil through capillary action, ensuring a steady supply of moisture to the plant roots.
- Reduced Watering Frequency: The passive wick system reduces the frequency of watering required, as it provides a continuous moisture supply to the plant.
- Ideal for Some Plants: It's particularly beneficial for plants that prefer consistently moist soil, such as certain tropical species.
- Maintenance: Regular checks on the water reservoir and wick condition are essential for optimal functioning of the passive wick system.
Capillary Action Pots
The passive wick system, commonly employed in plant containers, operates through capillary action to facilitate a steady supply of moisture to the soil, and from this framework, the discussion now shifts to capillary action pots, a type of self-watering system.
Capillary action pots utilize the natural capillary forces in the soil to draw water from a reservoir into the root zone of plants. This method offers several benefits, including consistent moisture levels, reduced watering frequency, and prevention of waterlogging. However, drawbacks such as potential salt buildup and uneven water distribution can occur, necessitating careful monitoring. Capillary action in gardening harnesses the principles of fluid dynamics to create a self-sustaining watering system, providing a practical solution for maintaining optimal moisture levels in potted plants.
| Capillary Action Pots | |
|---|---|
| Benefits | – Consistent moisture levels |
| – Reduced watering frequency | |
| – Prevention of waterlogging | |
| Drawbacks | – Potential salt buildup |
| – Uneven water distribution |
Reservoir Planters
Reservoir planters, also known as self-watering containers, utilize a built-in water reservoir to provide a consistent and controlled supply of moisture to the soil, offering several advantages for plant health and maintenance.
These types of planters offer benefits such as:
- Enhanced Plant Health: Reservoir planters ensure that plants receive a consistent water supply, preventing both under and overwatering, which can be detrimental to plant health.
- Reduced Watering Frequency: The reservoir allows for a slower water release, reducing the frequency of watering needed, which is particularly beneficial for busy individuals or those with a large number of plants.
- Prevention of Waterlogging: The design of the reservoir helps prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot and other issues.
- Proper Reservoir Maintenance: Regular cleaning and maintenance of the reservoir are essential to prevent the buildup of algae, bacteria, or mineral deposits that could affect plant health.
Proper reservoir maintenance is crucial for maximizing the benefits of these planters.
Factors Affecting Plant Health

Considering various environmental factors is crucial for understanding their impact on plant health. Factors affecting plant health, such as watering frequency, play a significant role in the overall well-being of plants. Adequate watering is essential for plant growth and development. Insufficient watering can lead to wilting, leaf drop, and stunted growth, while overwatering can cause root rot and other diseases. Finding the right balance is key.
Factors such as humidity, temperature, and light exposure also influence plant health. Humidity levels affect transpiration rates and water uptake, while temperature influences metabolic processes. Furthermore, light exposure affects photosynthesis, which is crucial for plant growth.
It is essential to monitor these factors to ensure optimal plant health. By understanding the interplay of watering frequency, humidity, temperature, and light exposure, one can create an environment conducive to plant growth. Additionally, different plant species have varying requirements, so it's important to consider the specific needs of each plant.
Choosing the Right Potting Mix

When selecting a potting mix for our plants, it's important to consider the different types available, their water retention capabilities, and the nutrient availability they offer.
The composition of the potting mix can greatly influence the overall health and growth of our plants. Understanding these factors will enable us to choose the most suitable potting mix to support the specific needs of our plants.
Potting Mix Types
Selecting the appropriate potting mix is crucial for ensuring the optimal growth and health of your plants in self-watering pots. The potting mix composition directly affects the plant's ability to absorb water and nutrients effectively, impacting watering frequency and overall plant health.
When choosing a potting mix for self-watering pots, consider the following:
- Peat-based Mixes: These mixes, often containing peat moss, are lightweight and retain moisture well, making them suitable for self-watering pots.
- Coconut Coir Mixes: Made from coconut husks, these mixes have excellent moisture retention and aeration, promoting healthy root growth.
- Vermiculite/Perlite Mixes: These mixes improve aeration and drainage, preventing waterlogging in self-watering pots.
- Composted Bark Mixes: Ideal for promoting drainage, these mixes are suitable for plants that prefer drier conditions.
Water Retention
To ensure optimal water retention and root health in self-watering pots, the choice of potting mix plays a critical role in providing the necessary balance of moisture and aeration for plant growth.
The soil composition directly affects water retention, with a mix that includes materials like peat moss, coconut coir, or vermiculite aiding in moisture retention. These components help to maintain adequate moisture levels within the potting mix, supporting plant hydration.
Furthermore, the evaporation rates within the potting mix are influenced by its composition, affecting the overall moisture levels available to the plant. Therefore, selecting a potting mix with a balanced combination of water-retentive and well-draining components is essential for promoting healthy root development and overall plant growth in self-watering pots.
Nutrient Availability
The potting mix composition not only impacts water retention but also significantly influences the availability of essential nutrients for plant growth in self-watering pots. When choosing a potting mix for self-watering pots, it's crucial to consider its impact on nutrient availability. Here are the key factors to consider:
- Nutrient Absorption: The potting mix should facilitate the absorption of essential nutrients by the plant's roots. Look for mixes that contain components like perlite or vermiculite, which can improve nutrient retention and absorption.
- Balanced Nutrient Content: Select a potting mix that provides a balanced blend of essential nutrients to support healthy plant growth. This ensures that the plants have access to all the necessary elements for their development.
- Watering Frequency: The potting mix shouldn't hinder the watering frequency required by the specific plant species. It should maintain a balance between retaining moisture and allowing proper drainage to avoid nutrient leaching.
- pH Balance: Consider the pH level of the potting mix, as it can affect nutrient availability. Ensure the mix's pH is suitable for the plants you intend to grow, promoting optimal nutrient uptake.
Choosing a potting mix that addresses these factors will promote efficient nutrient availability for your plants in self-watering pots.
Maintenance and Care Tips

When caring for self-watering pots, it's essential to regularly check the water level and ensure that the reservoir is clean to prevent any potential issues with mold or bacteria growth.
The watering frequency depends on various factors such as the type of plant, soil type, and sunlight exposure. It's crucial to monitor the soil moisture and adjust the watering frequency accordingly to avoid overwatering or underwatering.
The soil type plays a significant role in determining the drainage and water retention capabilities, affecting the self-watering pot's performance. It's important to use well-draining soil to prevent waterlogging and root rot.
Additionally, considering the sunlight exposure is vital as it affects the evaporation rate and the plant's water requirements. Regularly inspecting the drainage system and cleaning it can prevent clogging and ensure proper water flow.
Furthermore, adequate sunlight exposure helps maintain a healthy balance of moisture in the pot. By following these maintenance and care tips, one can ensure the optimal functionality of self-watering pots, promoting the well-being of the plants they contain.
Impact on Root Development

Examining the impact of self-watering pots on root development reveals the crucial role of consistent moisture levels in fostering healthy and robust root systems.
1) Impact of overwatering: Self-watering pots, if not used correctly, can lead to overwatering, which deprives the roots of essential oxygen and can cause root rot. It's important to monitor the moisture levels to prevent overwatering.
2) Oxygen availability: Overwatering in self-watering pots can limit the availability of oxygen to the roots, hindering their development. Proper drainage and aeration are crucial to prevent this issue.
3) Root system development: Consistent moisture provided by self-watering pots can support the development of a well-distributed and extensive root system, promoting overall plant health.
4) Nutrient uptake: Adequate moisture levels facilitated by self-watering pots can enhance the root's ability to uptake essential nutrients, contributing to the plant's growth and vitality.
Understanding the impact of self-watering pots on root development underscores the importance of proper usage and monitoring to avoid potential issues such as overwatering and ensure optimal root growth.
Common Misconceptions

Contrary to popular belief, self-watering pots are often misunderstood and subject to common misconceptions regarding their impact on plant health and maintenance.
One common misconception is that self-watering pots lead to overwatering. However, when used correctly, these pots provide a consistent moisture level, preventing both overwatering and underwatering.
Another misconception is that self-watering pots are maintenance-free. While they reduce the frequency of watering, monitoring water levels and occasional cleaning are still necessary for optimal plant health.
Additionally, some believe that self-watering pots are only suitable for certain types of plants. In reality, a wide variety of plants, including herbs, vegetables, and ornamentals, thrive in self-watering pots.
Furthermore, there's a misconception regarding the impact of self-watering pots on plant health. Some people believe that these pots can lead to root rot due to excessive moisture. However, self-watering pots are designed to prevent waterlogging and provide aeration to the roots. When used correctly, they can actually promote healthier root systems by ensuring consistent moisture levels and reducing stress on the plants.
Best Plants for Self-Watering Pots

Self-watering pots, often misunderstood and subject to common misconceptions, can effectively support a variety of plants, including herbs, vegetables, and ornamentals, making them suitable for a wide range of botanical species.
When choosing plants for self-watering pots, it's important to consider their water needs and growth habits. Here are some ideal plants for self-watering pots:
- Herbs: Herbs like basil, parsley, and mint thrive in self-watering pots. Their shallow root systems are well-suited to the consistent moisture provided by these pots, making them perfect for indoor herb gardens.
- Succulents: Many succulents, such as aloe vera and echeveria, can thrive in self-watering pots due to their ability to store water in their leaves and stems. Proper succulent care involves using well-draining soil and allowing the potting mix to dry out between watering, which can be effectively managed in self-watering pots.
- Vegetables: Compact vegetables like cherry tomatoes, peppers, and lettuce are well-suited for self-watering pots, making them ideal for container gardening in small spaces.
- Ornamentals: Plants like peace lilies, pothos, and spider plants are excellent choices for self-watering pots, particularly for indoor plants, as they can thrive with consistent moisture and controlled watering.
Choosing the right plants for self-watering pots can maximize the benefits of these containers, providing an efficient and low-maintenance solution for nurturing a variety of botanical species.
Environmental Considerations

When considering environmental impact, it's important to evaluate the water efficiency and potential for reducing overall water consumption when utilizing self-watering pots for plant cultivation.
Self-watering pots have the potential to minimize water wastage through their unique design, which allows for the gradual and efficient delivery of water directly to the plant's roots. This can lead to reduced water usage compared to traditional watering methods, contributing to water conservation efforts.
Additionally, the controlled irrigation provided by self-watering pots helps prevent water runoff and evaporation, further enhancing their water-saving capabilities.
From an environmental standpoint, the use of self-watering pots can positively impact water conservation by promoting efficient water usage. By minimizing water wastage and supporting sustainable irrigation practices, these pots offer a practical solution for individuals seeking to reduce their environmental footprint.
However, it's essential to consider the materials used in the production of self-watering pots and their potential environmental impact. Selecting pots made from eco-friendly and recyclable materials can further enhance the positive environmental aspects of self-watering pot usage.
Therefore, when used responsibly and in conjunction with eco-conscious practices, self-watering pots can contribute to environmental sustainability and water conservation efforts.
Tips for Successful Use

To ensure successful use of self-watering pots, it's important to monitor the soil moisture regularly and adjust the watering frequency based on the specific needs of the plant. Here are some tips for maximizing the benefits of self-watering pots:
- Proper watering frequency: Understand the water requirements of your plants and adjust the watering frequency accordingly. Different plants have varying needs, so it's crucial to tailor the watering schedule to each specific plant.
- Choose the right pot size: Select a pot size that's appropriate for the plant's root development. A pot that's too large can lead to overwatering, while a small pot may not provide adequate space for root expansion.
- Understand the watering mechanism: Familiarize yourself with how the self-watering mechanism of the pot works. This will help you make necessary adjustments and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
- Consistent monitoring: Regularly check the soil moisture and the effectiveness of the drainage system to ensure that your plants are receiving the right amount of water. Consistency in monitoring and adjusting the watering schedule is essential for the overall health of the plants.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Self-Watering Pots Suitable for All Types of Plants?
Choosing the right plants for self-watering pots is crucial. Some plants, like succulents, prefer drier soil, so they may not thrive in these pots.
Proper maintenance involves monitoring water levels to prevent overwatering. It's essential to consider the specific watering needs of each plant to ensure their health and growth.
With the right plant selection and attentive care, self-watering pots can be suitable for a wide variety of plants.
Can Self-Watering Pots Lead to Overwatering and Root Rot?
Self-watering pots have potential disadvantages, like overwatering and root rot if not properly maintained. Proper maintenance involves monitoring the soil moisture and adjusting watering frequency based on plant needs. This ensures that the plants receive the right amount of water and reduces the risk of overwatering.
Understanding the specific requirements of different plant species is crucial for successful use of self-watering pots.
Are Self-Watering Pots Suitable for Outdoor Use in Different Climates?
When it comes to outdoor container gardening, the soil moisture in outdoor planters is critical to plant health. Different climates may require varying watering systems for outdoor use.
Self-watering pots can be suitable for outdoor use in various climates, as they provide a consistent water supply to plants. However, it's important to monitor soil moisture levels to ensure the plants receive the appropriate amount of water and avoid issues like overwatering and root rot.
Do Self-Watering Pots Require a Specific Type of Water to Function Effectively?
We've found that the water quality used in self-watering pots can greatly impact their effectiveness.
The type of water can affect the functionality of the pot and the health of the plants.
It's essential to consider the mineral content, pH levels, and potential contaminants in the water.
Additionally, the specific needs of the plants should be taken into account to ensure compatibility with the self-watering system.
Can Self-Watering Pots Attract Pests or Mold?
We've found that self-watering pots can potentially attract pests or mold if not properly maintained. To mitigate this, regular cleaning and maintenance is crucial.
Additionally, using a well-draining potting mix and avoiding overwatering can help prevent mold growth.
Common misconceptions include that self-watering pots eliminate all maintenance, but in reality, they require regular upkeep to avoid these potential drawbacks.
Understanding these maintenance tips is essential for reaping the benefits while minimizing the drawbacks.
Are Self Watering Pots Durable and Long Lasting?
Yes, self watering pots are durable and long lasting. When properly maintained, self watering pots can last for several years. The key to maximizing their lifespan is to follow the manufacturer’s instructions on how long self watering pots last and to regularly clean and inspect the pots for any signs of wear and tear.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while self-watering pots offer convenience and benefits for plant care, it's important to consider the potential risks and factors affecting plant health.
Understanding the different types of self-watering systems and choosing the right plants for these pots is crucial.
As we continue to explore the environmental considerations and tips for successful use, it's clear that self-watering pots can be both beneficial and challenging for plant care.
Stay tuned for more insights and recommendations on maximizing the benefits of self-watering pots.










